Imagine a doctor trying to jot down every detail about a patient during a busy day. It’s time-consuming and takes focus away from the patient. Now, imagine the doctor just speaks, and all the details are automatically recorded and organized in their system. That’s the magic of voice technology in EMR (Electronic Medical Records).
Voice technology in EMR lets doctors and nurses use their voices to input patient information instead of typing or writing it down. This isn’t just a fancy microphone—it uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) to understand medical terms and accurately record data.
Think of it as a smart assistant. You speak, and it does the work, freeing up your hands and brain for what matters most: patient care.
Voice-enabled EMR systems bring transformative benefits to healthcare professionals by optimizing time management, reducing errors, and enhancing patient care. Below is an in-depth explanation with practical scenarios in a table format.
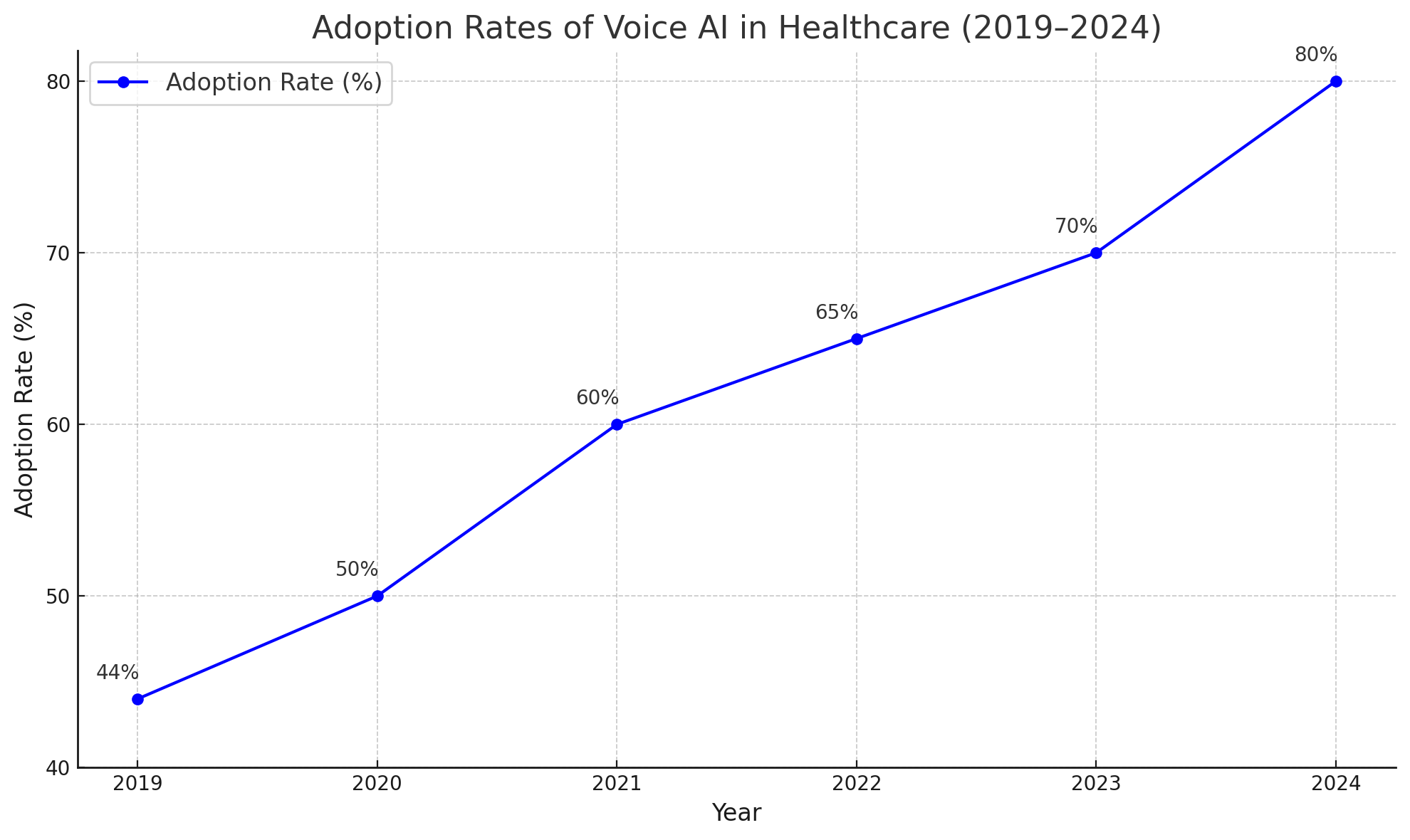
Doctors and nurses often spend hours entering data manually. With voice-enabled systems, they can complete these tasks in a fraction of the time by simply speaking their notes.
| Scenario | Manual Data Entry (Time Taken) | Voice-Enabled EMR (Time Taken) |
| Updating patient history | 5 minutes | 1 minute |
| Entering medication instructions | 3 minutes | 45 seconds |
| Documenting follow-up instructions | 4 minutes | 1 minute |
When a nurse says, “Prescribe 500 mg of Amoxicillin twice daily for 7 days,” the system cross-checks for errors, ensuring accuracy in dosage and duration.
→ A doctor dictates, “Patient history includes diabetes, hypertension, and recent surgery for appendicitis.”
→ The system records and organizes this in the EMR instantly, reducing the time spent typing and navigating forms.
Manual typing often leads to typos or incomplete entries, especially during busy shifts. Voice-enabled systems, powered by AI, ensure better accuracy by understanding medical terminology and structured data entry.
| Common Error | Manual Entry Risk | Voice Technology Advantage |
| Typos in medication names (e.g., Metoprolol → Metoprolol) | High | Low |
| Missing fields in patient records | Medium | Minimal |
| Misinterpretation of shorthand (e.g., HTN for hypertension) | High | Minimal |
When a nurse says, “Prescribe 500 mg of Amoxicillin twice daily for 7 days,” the system cross-checks for errors, ensuring accuracy in dosage and duration.
Voice technology allows doctors to focus on patients rather than screens, improving communication and care quality.
| Aspect | Without Voice Technology | With Voice Technology |
| Eye contact during consultations | Reduced (due to typing) | Maintained |
| Patient satisfaction | Lower | Higher |
| Ability to address patient concerns promptly | Delayed | Immediate |
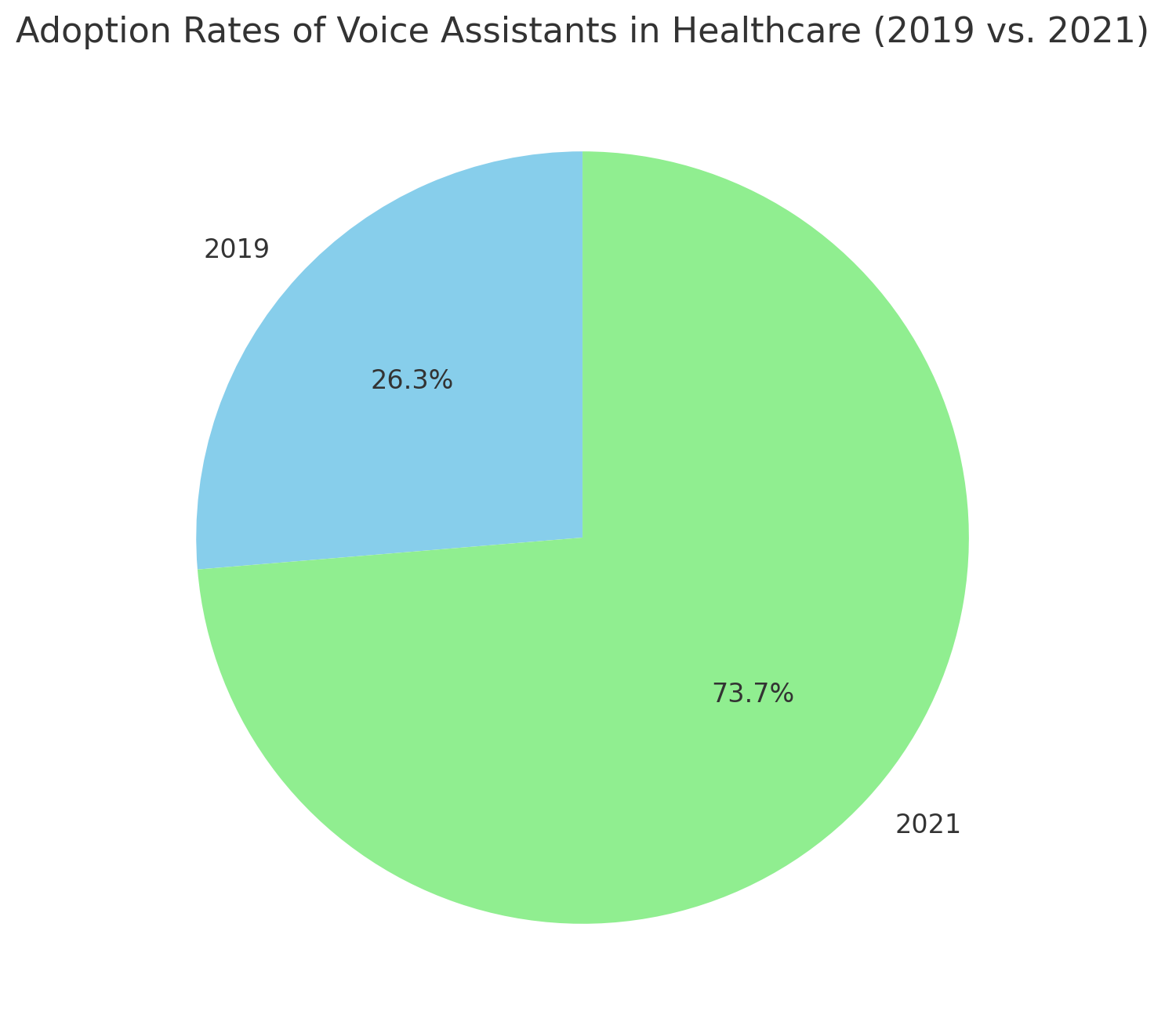
While voice technology in EMR offers significant advantages, it does come with some hurdles that healthcare providers must address to maximize its potential.
1. Background Noise
Hospitals and clinics are often bustling with activity. Conversations, equipment alarms, and other ambient sounds can interfere with the system’s ability to recognize and accurately process voice commands. This can lead to delays or incorrect entries.
Example:
A doctor dictating “Administer 5 milligrams of medication” might be misheard as “Administer 50 milligrams” due to surrounding noise. Ensuring a quieter environment or using noise-cancellation features in the system can help mitigate this challenge.
2. Learning Curve
Introducing voice technology requires time for healthcare providers to adapt. Some may find it challenging to adjust from traditional typing or writing methods to speaking commands into a system.
Solution:
Regular training sessions and user-friendly interfaces can ease this transition. For example, providing a step-by-step tutorial on dictating notes or commands can build confidence among users.
3. Accuracy Issues
Medical terminology is complex, and if the system isn’t thoroughly trained, it may misinterpret specific terms or abbreviations. This could result in errors in patient records or treatment instructions.
Mitigation:
Advanced Natural Language Processing (NLP) and regular updates to the system’s database can improve accuracy. For instance, training the system with commonly used medical terms and their variations can significantly reduce errors.
Voice technology in EMR is evolving rapidly, driven by advancements that make it smarter, more accurate, and easier to use. Let’s explore the key technological developments:
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enables voice systems to understand medical terminology and context better. It ensures that when a doctor says “prescribe 50 mg of Metoprolol twice a day,” the system accurately captures and records it in the EMR without confusion.
2. Ambient Listening
Modern systems use ambient listening to operate seamlessly in the background. This means they can capture important information from a conversation without needing a command to start.
3. AI Training for Medical Contexts
AI models powering these systems are now trained with vast amounts of medical data, ensuring they can handle complex scenarios. For instance, recognizing variations of a term like “hypertension” and “high blood pressure” as the same condition.
Voice technology in EMR is becoming smarter and more advanced, with exciting developments on the horizon.
1. Integration with Wearables
Voice systems will work alongside devices like smartwatches and fitness trackers. These devices will collect health data, like heart rate or sleep patterns, and send it directly to EMRs.
Example: A smartwatch detects an irregular heartbeat and updates the doctor’s records automatically, allowing for quick action.
2. AI-Driven Insights
Future voice systems won’t just record data—they’ll analyze it. By spotting patterns and trends, these systems can suggest possible diagnoses or next steps.
Example: A doctor describes a patient’s symptoms, and the system flags them as early signs of diabetes, recommending further tests.
3. Multilingual Support
Voice technology will break language barriers by supporting multiple languages and dialects. This will make healthcare more accessible worldwide.
Example: A doctor in Spain can speak to the system in Spanish, while a nurse in India can use Hindi, all on the same platform.
Voice-enabled EMR systems handle sensitive health data, making privacy and security critical.
Healthcare providers must choose voice technology solutions that prioritize security and follow strict legal standards to protect patient trust.
Voice-enabled EMR systems bring significant advantages over traditional manual data entry methods. Let’s break it down practically in a table format:
| Aspect | Voice Technology | Manual Data Entry |
| Speed | Doctors and nurses can speak faster than they can type, completing tasks quickly. | Typing or writing takes more time, especially for detailed records. |
| Accuracy | Voice systems trained with AI reduce errors, especially in medical terminology. | Accuracy depends on the individual’s typing skills and familiarity with the EMR. |
| User Effort | Minimal effort—users speak naturally, and the system records automatically. | High effort—requires full attention and manual interaction with the system. |
| Cost Efficiency | Long-term savings through automation and reduced reliance on administrative staff. | Higher costs due to the time and labor required for manual data entry tasks. |
| Error Detection | AI flags inconsistent or incomplete entries during dictation. | Errors may go unnoticed until later reviews, potentially delaying corrections. |
| Focus on Patients | Doctors spend more time interacting with patients as they dictate during consultations. | Doctors often divert attention to screens, reducing direct patient engagement. |
Voice technology is changing the game for EMR data entry. It saves time, reduces errors, and allows doctors to focus on their true job—caring for patients. While there are challenges, ongoing advancements in AI and privacy measures ensure this technology will continue to grow.
The future of healthcare is here, and it’s as simple as speaking your mind.
IoT Insights and Latest Trends